The stack of papers hit my desk like a ton of bricks. These files were faxes received from other vet clinics containing the records for two dogs that I was to see for a "5th opinion". There were two malamutes in the same family with a large history of dermatopathology (skin disease). When presented with such a case, I tend to go a little goofy.
First off, derm disease is fiendishly difficult and expensive to treat with the tools that we have available to us. Owners most often get frustrated long before completely exhausting options, and even when we have the diagnosis nailed maintenance of these dogs can be extremely difficult. Our professors back in school used to tell us that derm disease would be the number one reason that clients would seek out a second opinion (or fifth opinion)
Secondly, what the heck was I going to find that four other veterinarians could not? I don't hold myself in such esteem as to think that what had evaded a number of other experienced veterinarians would be painfully obvious to me. The records were all over the board; skin scrapings, food trials, antibiotics, antifungals, Veterinary Information Network threads about zinc responsive dermatitis, etc. It seems that pretty much anything I could think of had been tried.
I made note of the receptionist that decided to put this heap in my column... it had just become obvious that she didn't really like me all that much. All joking aside there was little in the stack of files to make me hopeful that I was going to make any difference in these dogs' lives.
When Balou and Tundra hit the doors with their owners, everyone cringed. They looked awful. There was little hair to be seen on Balou, and his sister Tundra was heading that way. You could see depression in their eyes. They had the look of a couple dogs that were just not enjoying life and had not been for some time. I sent in my assistant to get a history while I worked on another patient... not at all looking forward to this.
 |
| Balou at his first visit to ITAH |
The assistant came out of the room with an obvious assessment; the dogs look like hell. Beyond that, the story became much more interesting. To my relief the owners were very nice, realistic, and observant. These three qualities make the veterinarian-client-patient relationship rewarding for all. They described a progression of disease that started with the introduction of Tundra to the family via a rescue organization. Previous veterinarians had done skin scrapings for mites, and had given mite treatments to one but not both dogs. Antibiotics and antifungals were of limited use, as were shampoos and novel foods. These dogs were itchy to the point of self mutilation and nothing really seemed to make a whole lot of difference.
The number one nagging part of the history which I just couldn't let go was the fact that it all started after Tundra arrived. It just screamed infectious. It screamed sarcoptic mange. The only issue was that the mites were not seen on previous skin scrapings, and they had technically been treated to no avail.
I started discussing differentials, and told them I just couldn't let go of the idea of mites. I decided to do another skin scraping. Sarcoptic mange is caused by the burrowing mite,
Sarcoptes scabiei. The mite is very difficult to find via skin scraping. Frequent false negatives are a hallmark of infestation. Whenever veterinarians suspect the disease, we treat for it... which had sort of been done already. Balou and Tundra had both received ivermectin and Frontline a couple times during their workup.
I chose two spots on Tundra and three spots on Balou for scraping. I had three slides and a whole lot of wishful thinking. If I didn't find the mites, I didn't know exactly what I was going to do. Should I try treating again? Would the owners go for it? What should I do in the mean time?
Luck was on my side that day, and I found one little mite on one of the slides (and I checked for a good 15 minutes before I found it). Bingo. This was what we were looking for. We could throw out everything else about the case, and deal with the devil we knew.
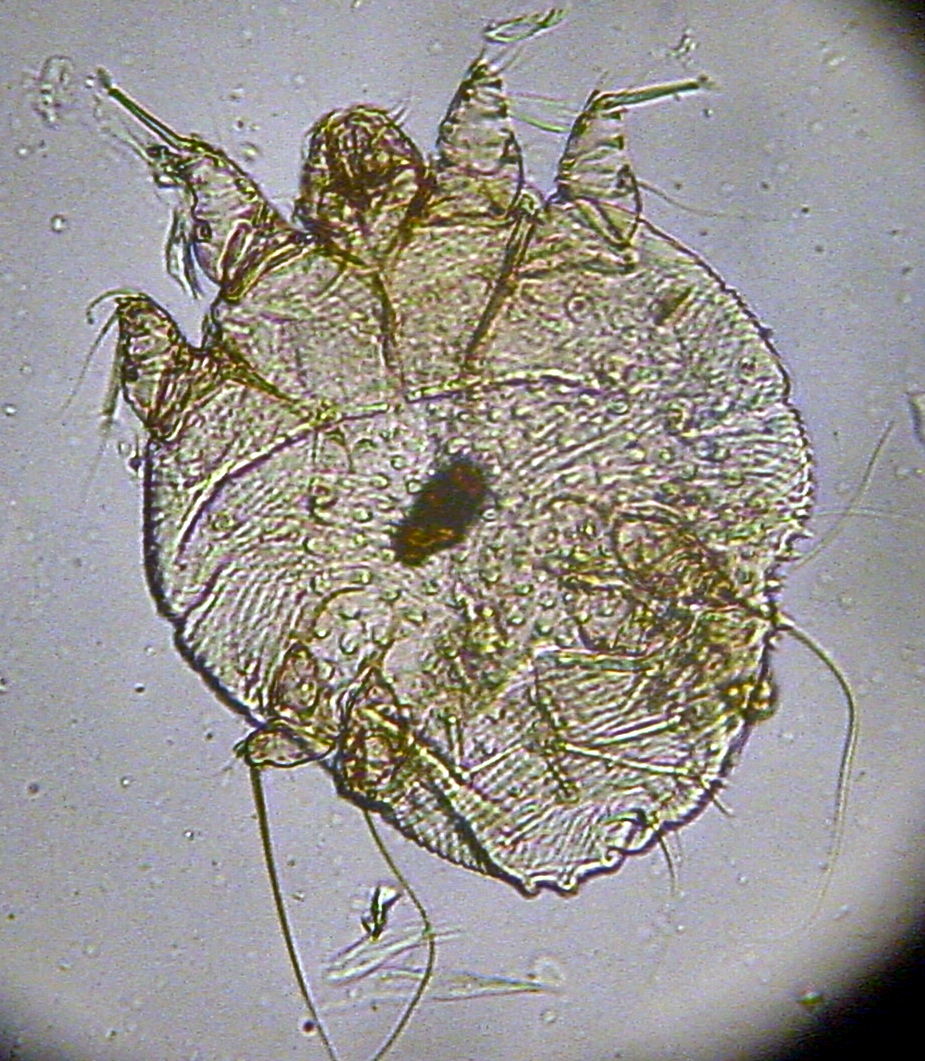 |
| Sarcoptes scabiei (from wikipedia) |
I went back into the room elated, and told the owners who were similarly elated. This was the best of all possible outcomes. Sarcoptic mange is a curable disease. I explained that I thought we should probably be a little more aggresive this time and treat both dogs concurrently with ivermectin injections and topical Frontline.
Upon further research I found that with very advanced cases of Sarcoptic mange, 6 weeks of treatment are needed to fully kill off the mites. We set a schedule of weekly injections. The difficulty in treating mange is that it is the immune system's reaction to the dead and dying mites that causes the worst signs. In severe cases, the patient will appear worse rather than better during the initial treatment, leading the clinician and owner to think that treatment is failing. Complicating this is the fact that most of the time we don't have a definitive diagnosis when we are treating.
 |
| Balou after 6 weeks of treatment |
After 6 weekly injections of ivermectin, the dogs were obviously looking and feeling much better. Within two weeks of stopping treatment, Balou returned with some sores on his paws and red irritated skin. I performed another skin scraping and did not see any mites. Tundra, it was reported, was back to normal. I was faced with a dilemma again... is this failure of treatment? Does he concurrently have some other skin disease? What to do?
Everything I have ever learned about Sarcoptic mange from texts and the Veterinary Information Network said that after 6 weeks of treatment, the mites should be gone. Anything that pops up after that should be considered a different problem.
However, the severity of disease on initial presentation made me want to just extend treatment another 6 weeks. We gave Balou another ivermectin injection and ordered a whole new bottle for the owners. His skin improved within a couple days, and the owners continued weekly ivermectin treatments for 6 more weeks.
I have seen him a couple times since that day, and every time he looked like a whole new dog. However, the most recent time I saw him was the most striking. He is one of the most beautiful dogs I have seen. He has all of his hair back (with the exception of a little bit on his tail), and he feels terrific.
 |
| Balou's most recent photograph |
Balou and Tundra's story was a big lesson for me and one of my proudest moments as a veterinarian. Rarely can we offer a complete cure for such a striking disease. Sarcoptic mange is extremely difficult to deal with. It is sneaky, and like so many other things in medicine, does not always act in accordance with the books.
I know that if I had not seen the little mite with my own eyes, I would not have stayed the course with treatment for as long as I did. Plagued with doubt and second-guessing, I would have been grasping at straws with exotic diseases and arcane treatments. I would have been doctor number five with a few pages of my own stacked on top of the rest of the file on another veterinarians desk.